
Megan K. Jacobson explains the fight and what’s at stake at MSN: A Washington State Revolt Against the Gas-Stove Grabbers. Excerpts in italics with my bolds and added images.
Environmentalists have waged a campaign against natural gas, but users of this efficient, low-emission fuel are fighting back. A wide range of industry groups are backing Washington state’s Initiative 2066 to protect the right to choose natural gas.
By 2030, Washington is supposed to reduce carbon emissions to 45% below 1990 levels—one of its many overlapping climate goals. The state’s most recent energy plan declares that the cheapest route to meeting Olympia’s climate targets is to switch many uses of oil and gas to electric sources. Last year the Building Code Council amended the state energy code to make it prohibitively costly to install gas appliances in new buildings. In March the Legislature passed a law allowing the state’s largest natural-gas and electricity utility, Puget Sound Energy, to pass the costs of going green onto consumers and mandating the utility files a plan “to achieve all cost-effective electrification of end uses currently served by natural gas.”
To the Washington Hospitality Association and the Building
Industry Association of Washington, Initiative 2066’s cosponsors,
this sounded like an economic wrecking ball.
Anthony Anton, CEO of the hospitality association, says 84% of the restaurateurs he represents rely on natural gas. Remodeling to go electric is a “massive cost at a time where operators just can’t afford it,” he says. Some say the quality of their product would suffer, as some cooking methods, such as stir-frying, are difficult to perform on lower-heat electrical stoves. Most of the association’s members are very small businesses with substantial debt from Covid lockdowns.
The building association worries the new energy code will raise the state’s already high housing costs, locking out potential buyers. The code requires that new buildings meet a certain environmental “score.” Without the points from an electric heat pump, a builder will have to make up the difference with other green measures that run between $15,000 and $20,000 in a single-family home. “Every time they raise the price $1,000, it prices out another 500 Washington families,” says Greg Lane, the association’s executive vice president.
Dozens of varied industry groups support Initiative 2066. Each has its own reasons. The Washington Denturist Association worries about the expense of switching from propane- or gas-based equipment and a lack of reliable power. Most members are small businesses and it’s a good path for immigrant dentists whose credentials don’t carry over to the U.S.
The Washington State Tree Fruit Association (of which my paternal grandfather’s company, Apple King, is a member) is concerned about rising costs of refrigeration to keep produce fresh. A sudden power outage could be catastrophic for the state’s apple industry. Trade regulations for its top two export markets require that fruit be constantly refrigerated at a specific temperature for as long as 90 days.
The state’s cheapest energy plan would almost double electricity demand in Washington by 2050, putting an unprecedented strain on the grid. The only real option is to increase wind and solar generation, since the state’s plentiful hydroelectric capacity can’t do more without potentially threatening salmon. Wind and solar tend to falter in Washington in the winter, when energy demand peaks.
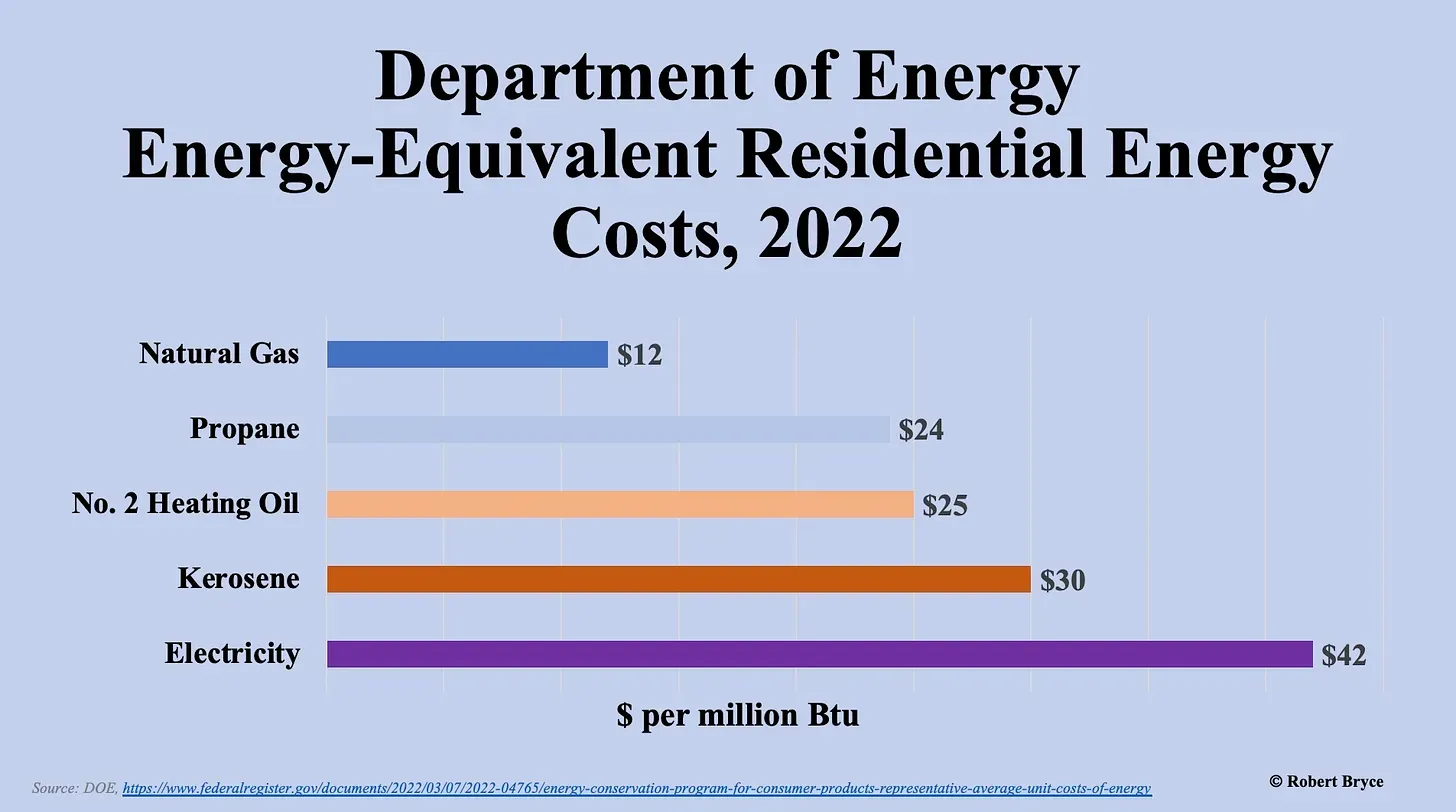
Consumers would also suffer in Washington’s green utopia. Everything from a haircut to a ballgame would become more expensive as the price of electricity rises. Climate advocates argue that Washingtonians will recoup their costs over time thanks to efficiency gains. But a 2021 report from Home Innovation Labs estimates that recovering the cost of a heat-pump installation could take 47 to 49 years. It’s worse for existing gas customers. The Building Industry Association of Washington estimates that switching from natural gas to electricity in a single-family home would cost as much as $70,000. Heat pumps also tend to fail in the sort of frigid weather that hits rural Washington in winter.
 Proponents of electrification insist that technology will improve over time. But if they’re really confident that green energy will be the best option for consumers and businesses, then Initiative 2066 is no threat. Washington voters should ask why climate advocates still see it as one.
Proponents of electrification insist that technology will improve over time. But if they’re really confident that green energy will be the best option for consumers and businesses, then Initiative 2066 is no threat. Washington voters should ask why climate advocates still see it as one.